Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of data storage, NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs have emerged as a game-changer, particularly for servers and data centers. NVMe SSDs offer unprecedented speed, efficiency, and versatility, addressing the growing demands of modern computing environments. This Tech Blog will explore the various form factors of NVMe SSDs and their significance in server applications.
Understanding NVMe SSD
NVMe is a high-performance, scalable host controller interface designed for PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) SSDs. Unlike traditional interfaces such as SATA and SAS, NVMe utilize PCIe bus to transmit data at a faster speed to and from SSD. Taking PCIe 4.0 x4 as an example, it can theoretically transport data at speeds of up to 8GB/s while SATA III’s maximum transfer rate is just 600MB/s. This results in dramatically improved input/output operations per second (IOPS) and reduced latency, making NVMe SSDs ideal for high-demand server environments.
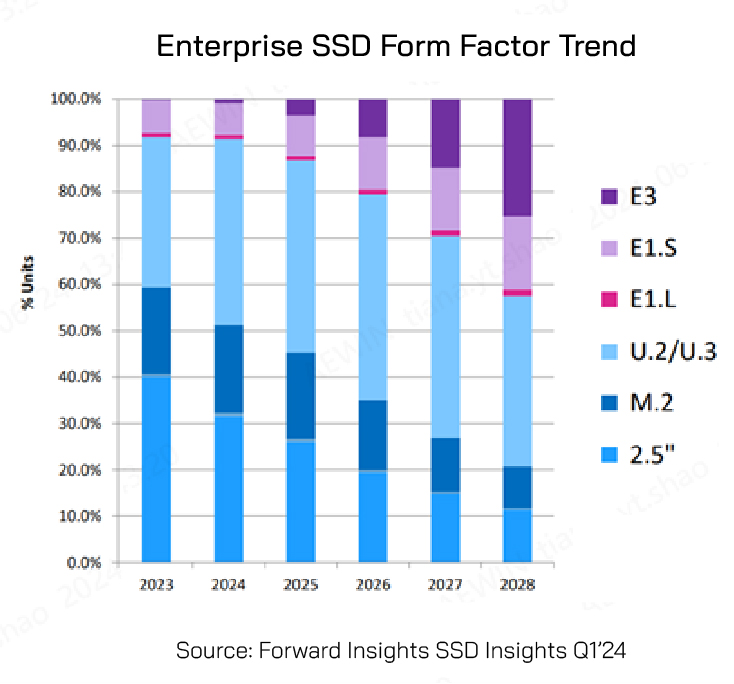
Featuring advanced performance and efficiency, NVMe SSDs have a variety of form factors—M.2, U.2, U.3, E1.S, E1.L, E3.S, and E3.L. Each of them offers unique benefits when they were released to the market. Forward Insights illustrates the trend of SSD form factor from 2023 to 2028 as below. It shows that NVMe SSD is taking the major lead of SSD market, and the main form factors of NVMe SSDs would be M.2, U.2, E3, and E1.S. Let us take a closer look at these main form factors of NVMe SSDs.
Major NVMe SSD Form Factors in Server Applications
Comparison Table*: M.2, U.2, E1.S, and E3.S
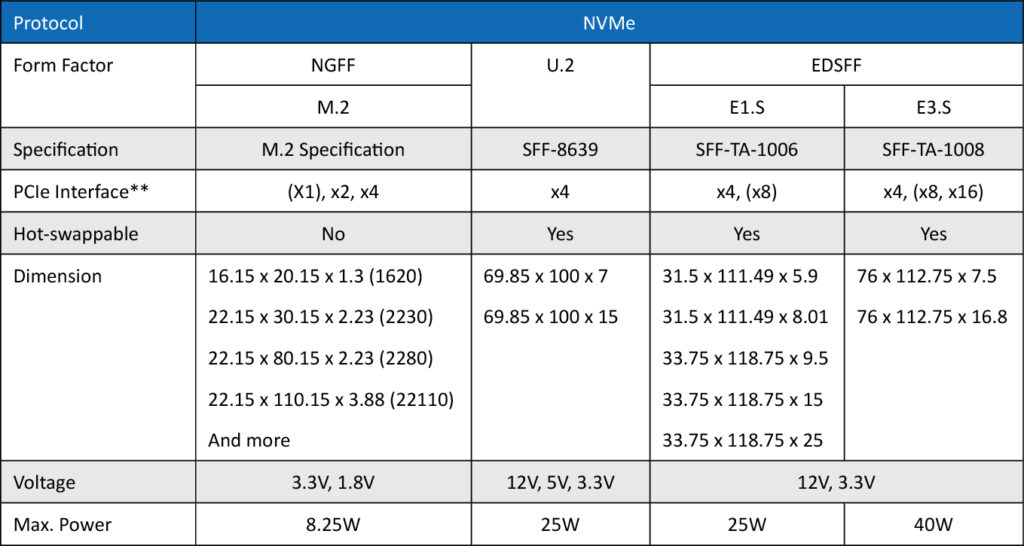
*: The information in the table is based on Specifications of SFF-TA-1006, SFF-TA-1008 from SNIA and M.2 Specification and SFF-8639 from PCISIG.
**: The PCIe interface listed in the table is defined by SNIA and PCISIG while the ones that is not commonly used is added with brackets.
– M.2
Next Generation Form Factor was renamed as M.2 in 2013 and has been applied widely to embedded systems and servers. M.2 NVMe SSD performs 1GB/s per lanes under PCIe Gen3 which has higher performance compared to SAS III having the limit of 600MB/s. Moreover, it also supports 2GB/s per lanes under PCIe Gen4 for enhanced bandwidth. However, it is facing problems of scaling due to its power limit and thermal constrains.
– U.2
U.2, previously known as SFF-8639, is a form factor of NVMe SSD that shares the same size of traditional SATA/SAS hard drives, 2.5”. U.2 NVMe SSDs leverage the PCIe bus, providing significantly higher data transfer speeds and lower latency compared to SATA and SAS interfaces. It provides dual port support offering greater resiliency for enterprise storage solutions. This makes U.2 a versatile and powerful option for various storage applications.
– EDSFF (E1.S, E3.S)
The Enterprise and Datacenter SSD Form Factor, EDSFF, has emerged in 2018 as a revolutionary standard designed to address the market needs, offering a versatile and optimized approach to storage in enterprise and data center environments. EDSFF is designed to replace traditional form factors like M.2 and 2.5-inch, providing a more efficient and scalable storage solution.
E1.S NVMe SSD features bigger power and better thermal management solution compared to M.2 which is the solution of the issue that M.2 is having. In addition, E1.S storage features hot-swappable to minimize downtime and perform easier maintenance for replacement or capacity upgrade.
Regarding 2.5” SSD use cases, it is about to migrate to E3.S storage for better performance as E3.S storage has higher power capabilities compared to U.2 (40W vs 25W) to support higher bandwidth of PCIe Gen5 or PCIe Gen6 in the future. In addition, E3 family provides dual port redundancy for enterprise SSDs to offer optimal data availability during system upgrades or failover events.
Summary
NVMe SSDs have revolutionized the storage landscape for servers, offering high speed, efficiency, and versatility. Understanding the various form factors and its features allows customers to select the best solutions most suitable to their needs. Whether optimizing for space, performance, or capacity, NVMe SSDs provide the options to meet the ever-increasing demands of modern data centers and enterprise environments.