
In our previous blog, we announced AEWIN SCB-1932C Server has been validated as a NVIDIA-Certified System for enterprise edge. Today we will explore more on the GPU benchmark tests across different AEWIN platforms.
System Configurations
Applying AEWIN High Performance Appliances, SCB-1946C, SCB-1932C, and SCB-1937C.
| Servers for Testing/Benchmark |
| System |
SCB-1946C |
SCB-1932C |
SCB-1937C |
Nvidia Benchmark |
| Processor |
Dual AMD EPYC 9174F
(Genoa) |
Dual Intel Xeon Gold 5318S
(Ice Lake) |
Dual AMD EPYC 7543
(Milan) |
Dual AMD EPYC 7003
(Milan) |
| Core |
16 |
24 |
32 |
N/A |
| Freq |
4.1 GHz |
2.1 GHz |
2.8 GHz |
N/A |
| Memory |
1x 32GB |
2x 32GB |
1x 32GB |
N/A |
| GPU |
1x Nvidia A30 |
1x Nvidia A30 |
1x Nvidia A30 |
1x Nvidia A30 |
| OS |
Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS |
Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS |
Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS |
N/A |
| Framework |
TensorRT 8.6.1 |
TensorRT 8.6.1 |
TensorRT 8.6.1 |
TensorRT 8.6.1 |
GPU Status Monitor
For preparation, write a GPU monitor script “monitor.sh” in the host in case of throttling.
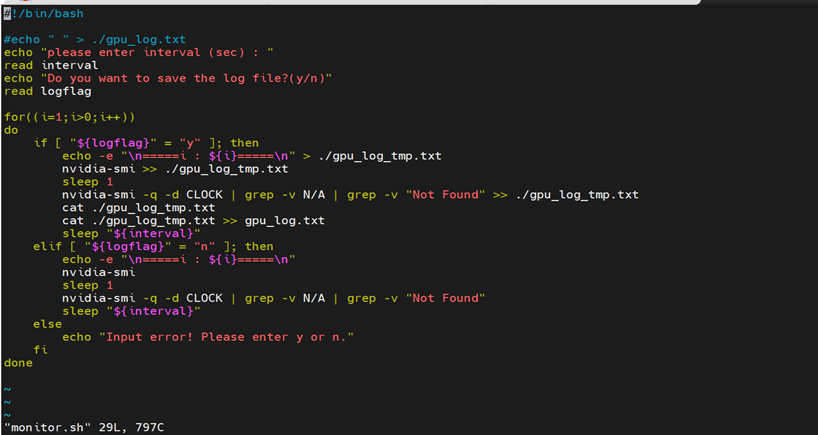
Input the status refresh duration as interval. input “y” to save log or “n” not to save log.
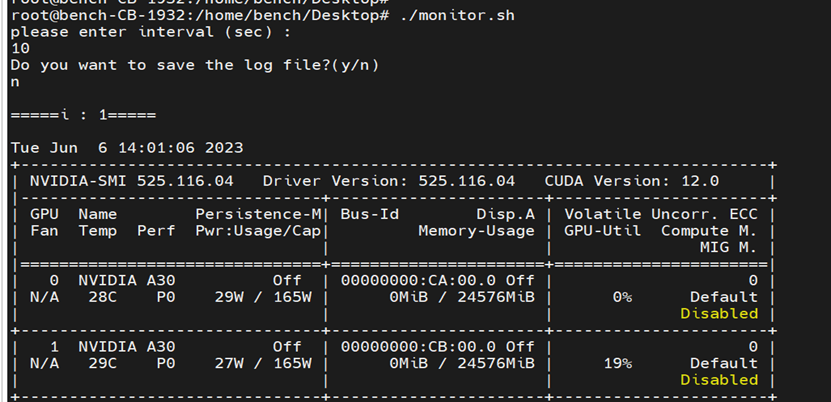
Benchmark Test
Run the script “benchmark.sh” from the host. It will redirect you to the GPU accelerated container. From the container run the script “benchmark.sh”. It will ask to choose between int8 mode or fp16 mode for the test. Input 1 to run in int8 mode.
Run the script “benchmark.sh” in the host to start the test. The picture below shows an example of the benchmark results.
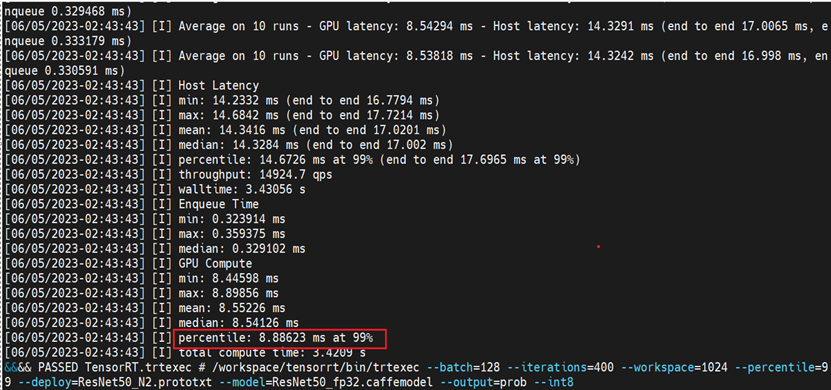
For the Benchmark results, we only consider the percentile value of the GPU Compute. For example, the percentile value shown in the above figure is equal to 8.88623. To calculate the performance in img/sec for any GPU, we use the following formula: 1000/(percentile/128), where 128 is batch size for current test. Thus, the int8 (images/sec) is equivalent to 14,405.
Testing Script
1. sh script in the container
#!/bin/bash
echo -e “for int8 test, press 1; for fp16 test, press 2 : ”
read testmode
if [ “${testmode}” -eq 1 ]; then
/workspace/tensorrt/bin/trtexec –batch=128 –iterations=400 –workspace=1024 –percentile=99 –deploy=ResNet50_N2.prototxt –model=ResNet50_fp32.caffemodel –output=prob –int8
elif [ “${testmode}” -eq 2 ]; then
/workspace/tensorrt/bin/trtexec –batch=128 –iterations=400 –workspace=1024 –percentile=99 –deploy=ResNet50_N2.prototxt –model=ResNet50_fp32.caffemodel –output=prob –fp16
else
echo -e “input wrong !!!”
fi |
2. sh script in the host
#!/bin/bash
docker run –gpus ‘”device=0″‘ -it –rm –name trt_2011 -w /workspace/tensorrt/data/resnet50/ trt:2011 |
3. burn-in script burn.sh in the container
#!/bin/bash
for((i=1;i>0;i++))
do
mpirun –allow-run-as-root -np 1 –mca btl ^openib python -u ./resnet.py –batch_size 128 –num_iter 28800 –precision fp16 –iter_unit batch
done |
4. burn-in script burn.sh in the host
#!/bin/bash
docker run –gpus ‘”device=0″‘ -it –rm –name tf_2011tf2 -w /workspace/nvidia-examples/cnn tf:2011tf2 |
5. GPU monitor script “monitor.sh” in the host
#!/bin/bash
#echo ” ” > ./gpu_log.txt
echo “please enter interval (sec) : ”
read interval
echo “Do you want to save the log file?(y/n)”
read logflagfor((i=1;i>0;i++))
do
if [ “${logflag}” = “y” ]; then
echo -e “\n=====i : ${i}=====\n” > ./gpu_log_tmp.txt
nvidia-smi >> ./gpu_log_tmp.txt
sleep 1
nvidia-smi -q -d CLOCK | grep -v N/A | grep -v “Not Found” >> ./gpu_log_tmp.txt
cat ./gpu_log_tmp.txt
cat ./gpu_log_tmp.txt >> gpu_log.txt
sleep “${interval}”
elif [ “${logflag}” = “n” ]; then
echo -e “\n=====i : ${i}=====\n”
nvidia-smi
sleep 1
nvidia-smi -q -d CLOCK | grep -v N/A | grep -v “Not Found”
sleep “${interval}”
else
echo “Input error! Please enter y or n.”
fi
done
|
Summary
As shown in the benchmark results, we verified A30 on the platforms including SCB-1946C(Genoa), SCB-1932C(Ice Lake), and SCB-1937C(Milan). They share better or similar results compared to Nvidia benchmarks.
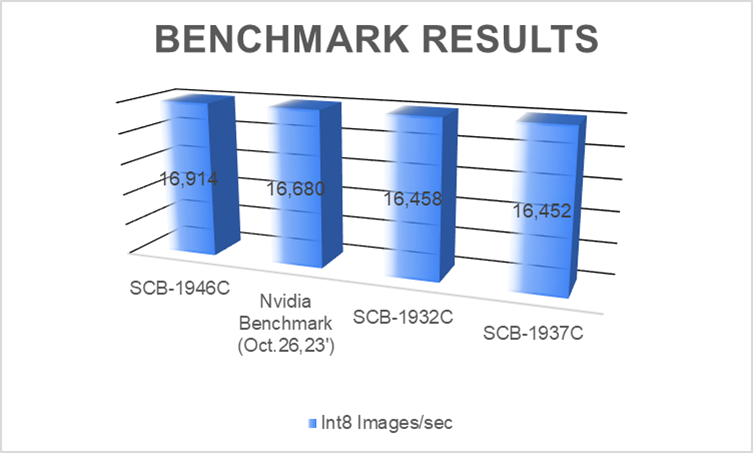
platforms range from edge AI appliances to general purpose computing systems, to high performance servers, customers can select the most suitable ones with the GPUs required for each application. Reach out to our friendly sales and discover more on AEWIN GPU Server platforms!
- SCB-1932: 2U Dual Ice Lake-SP PCIe 4.0 Platform with short depth design, 4x PCIe Gen4 slots plus dual FHFL GPU slots or 4x PCIe Gen4 NIC, and IPMI.
- SCB-1933: 2U Ice Lake-SP PCIe 4.0 Platform with short depth design, 4x PCIe Gen4 slots plus dual FHFL GPU slots or 4x PCIe Gen4 NIC, and IPMI.
- SCB-1942: 2U Dual Sapphire Rapids-SP PCIe 5.0/CXL Platform with short depth design, 4x PCIe Gen5 slots plus dual FHFL GPU slots or 4x PCIe Gen4 NIC, and IPMI.
- SCB-1943: 2U Sapphire Rapids-SP PCIe 5.0/CXL Platform with short depth design, 4x PCIe Gen5 slots plus dual FHFL GPU slots or 4x PCIe Gen5 NIC, and IPMI.
- SCB-1946: 2U Dual EPYC-9004 (Genoa/Bergamo) PCIe 5.0/CXL Platform with short depth design, 4x PCIe Gen5 slots plus dual FHFL GPU slots or 4x PCIe Gen4 NIC, and IPMI.
- SCB-1947: 2U EPYC-8004 (Siena) PCIe 5.0/CXL Platform with short depth design, 8x PCIe Gen5 slots NIC, NVMe, and IPMI.
- BAS-6101A: 2U High-Density Edge Computing Server with AMD Bergamo/Genoa/Genoa-X processor, total 8x PCIe slots (2x dual width FHFL PCIe Gen5 x16 or 4x single width FHFL PCIe Gen5 x16, 2x single width FHHL PCIe Gen5 x16, 2x HHHL PCIe Gen4 x8) + 1x OCP 3.0 slot for NICs and Accelerators.
- BAS-6101B: 2U High-Performance Server with AMD Bergamo/Genoa/Genoa-X processor, total 8x PCIe slots (2x dual width FHFL PCIe Gen5 x16 or 4x single width FHFL PCIe Gen5 x16, 2x single width FHHL PCIe Gen5 x16, 2x HHHL PCIe Gen4 x8) for NICs and Accelerators.